S1PR1 modulator 1
CAS No. 2328109-05-1
S1PR1 modulator 1( —— )
Catalog No. M26430 CAS No. 2328109-05-1
S1PR1 modulator 1 is a selective inhibitor of S1PR1 with a pIC50 of 7.6.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 110 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 156 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 257 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 380 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 563 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameS1PR1 modulator 1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionS1PR1 modulator 1 is a selective inhibitor of S1PR1 with a pIC50 of 7.6.
-
DescriptionS1PR1 modulator 1 is a selective inhibitor of S1PR1 with a pIC50 of 7.6.(In Vitro):S1PR1 modulator 1 shows >40- and >80-fold selectivity, over the other S1PR isoforms S1PR3 (pIC50, 6), S1PR2 and S1PR4 (pIC50s, <5).
-
In VitroS1PR1 modulator 1 (Compound 10a; (Z,Z)-10a) is selective at S1PR1 over S1PR3 (pIC50, 6), S1PR2 and S1PR4 (pIC50s, <5).
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorFungal| glucan synthase
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2328109-05-1
-
Formula Weight408.51
-
Molecular FormulaC23H24N2O3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
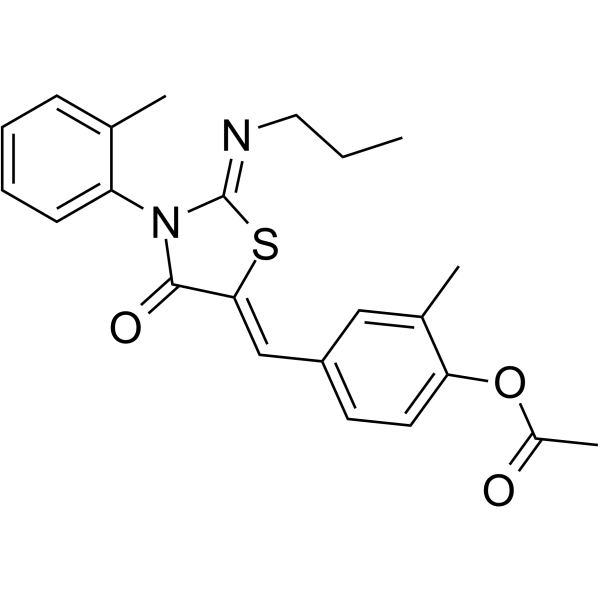
SMILESN(\CCC)=C\1/N(C(=O)\C(=C\C2=CC(C)=C(OC(C)=O)C=C2)\S1)C3=C(C)C=CC=C3
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Miesel L, et al. Efficacy of Rezafungin in Prophylactic Mouse Models of Invasive Candidiasis, Aspergillosis, and Pneumocystis Pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Feb 17;65(3):e01992-20.
molnova catalog



related products
-
SR9238
SR9238 is a synthetic agonist of liver X receptor inverse (IC50s: 214 nM and 43 nM for LXRα and LXRβ, respectively).
-
Tropic acid
Reference standards.
-
(-)-Pinoresinol 4-O-...
(-)-Pinoresinol 4-O-glucoside is a natural product from Lonicera japonica THUNB.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


